

Last Updated: 8/16/2024 | 13 min. read
Bittensor is a platform that helps facilitate the development of open and global artificial intelligence systems through the use of decentralized networks and economic incentives.
Summary
Bittensor stands at the forefront of two of the most groundbreaking, transformative trends in software: blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI). While Bitcoin helped create the crypto industry as the first peer-to-peer money system and a digital store of value and Ethereum helped to expand the ecosystem with decentralized applications, Bittensor represents an entirely new and distinct use case. It intends to harness the properties of permissionless, public blockchains and economic incentives to develop advanced AI software through an open, decentralized community (rather than a centralized company).
Today, AI development is highly centralized, with significant power concentrated in a few large tech companies. As AI continues to evolve into a more powerful and essential tool, we run the risk that the immense power of AI is controlled by a few entities and is not aligned with human values and the broader society. In contrast, Bittensor is a platform that economically incentivizes open collaboration of AI development through its native token, TAO. Through use of a public blockchain, Bittensor could potentially help democratize ownership and increase transparency around AI systems as well as align decisions regarding AI development with the interests of society. Bittensor aims to create the "Internet of AI," envisioning a future with many interconnected AI ecosystems, or subnets, that form a global decentralized AI platform. This platform would help enable anyone, anywhere, to easily build, deploy, and access artificial intelligence applications by connecting to the Bittensor network.
Exhibit 1: TAO represents 12% of the Grayscale AI Universe as of 8/16/2024[1]

The Token
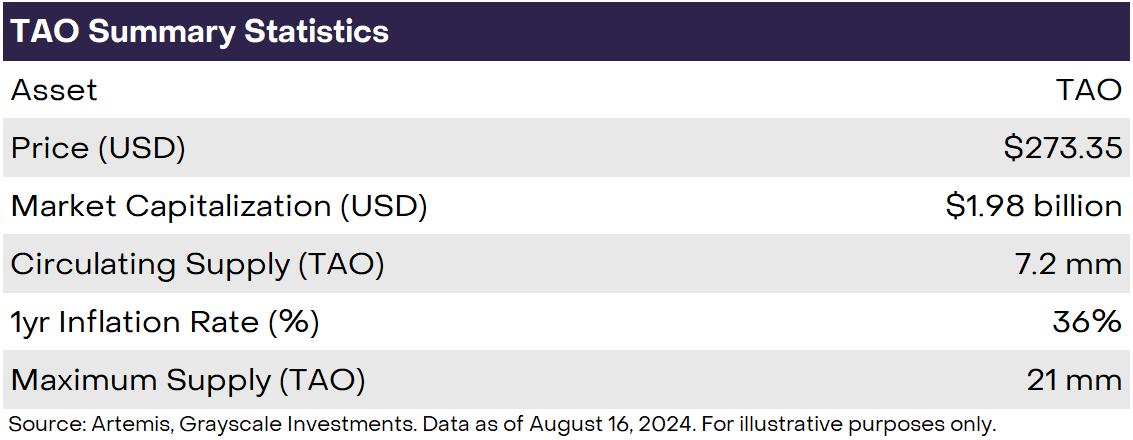
TAO is the native token of the Bittensor network and ownership of the TAO token represents a piece of ownership in the ecosystem (Exhibit 2). The TAO supply schedule directly mirrors that of Bitcoin, with a maximum supply of 21 million and a halving approximately every four years. Bittensor’s first halving event is expected to occur in August 2025.
Bittensor is intended to apply Bitcoin-style incentives to AI development, with the TAO token used as an incentive for network participants to perform their intended functions. These participants include network validators and subnetwork (subnet) owners, subnet validators, and subnet miners (these terms are defined in the next section). Beyond incentive rewards, TAO is primarily used today as a deposit fee for subnet owners registering their subnet. In the near future, as the nascent Bittensor network matures, potential additional use cases for TAO include (i) as gas fees for network transactions, (ii) as decision power over which subnets to allocate TAO emissions, and (iii) general network governance decisions. In the longer term, Bittensor may monetize its network by charging end-user applications that use its subnets; this would potentially generate value accrual back to the TAO token.
Exhibit 2: TAO token basics
The Network and Technology:
On Bittensor, developers compete to produce the best AI model outputs in exchange for TAO rewards. This system supports a range of AI-related services, including chatbots, video generation, deepfake detection, storage, and compute.[2] In an effort to democratize AI development, Bittensor allows AI researchers and independent open-source developers to monetize their innovations and potentially contribute to a more equitable distribution of AI benefits.
Bittensor employs a wide variety of subnets tailored to perform distinct machine-learning tasks. For example, one subnet is tailored to AI image generation, another is for AI music generation, and another is for detecting AI-generated deep fakes. Each subnet involves three primary types of actors: the subnet owner, subnet miners, and subnet validators. On a given subnet, miners compete to produce the “best” model outputs while validators assess which miners are the “best” performing (see below). Though elements of this process vary from subnet to subnet, the general idea is outlined below:
How It Works
(Examples provided for illustrative purposes only.)
Validators determine miner performance through a novel process known as Yuma consensus. This consensus mechanism aggregates the rankings of each validator, weighted by their amount of TAO staked, to produce a collective ranking list of miner performance.
The broader Bittensor blockchain operates under a “proof of authority” consensus mechanism where certain nodes are granted the authority to order on-chain transactions and help maintain the network's integrity. Bittensor’s blocks store updated state changes and token balances to reflect new emissions to network validators, as well as subnet owners, miners, and validators.
Use Cases
Bittensor has a wide range of potential use cases, with each subnet representing a different example. Examples include:
Among decentralized AI solutions in crypto, Bittensor has a few direct competitors that are addressing AI development holistically. For example,[3] the Allora network focuses on AI development in the financial services sector, serving as a platform for automated trading strategies for decentralized exchanges and prediction markets. Other early projects attempting to address decentralized AI on an infrastructure level include Sentient and Sahara AI.
In addition to these direct competitors, certain protocols compete with specific Bittensor subnets. For example,[4] Akash competes to some extent with the compute subnet, Filecoin competes with the data storage subnet, and Gensyn competes with pre-training and fine-tuning subnets. Still, some notable AI companies (e.g. Wombo and MyShell) and crypto teams (e.g. Masa, Kaito, and Foundry) have built their own subnets.
Factors to Consider
Investment Risks
[1] AI Universe as defined by the Grayscale Research. Assets must have a minimum market capitalization of $500mm. AI Universe is rebalanced quarterly and was rebalanced at 4/1/2024 and 7/1/2024. The assets in the AI Universe include NEAR, FET, RNDR, FIL, TAO, THETA, AKT, AGIX, WLD, AIOZ, TFUEL, GLM, PRIME, OCEAN, ARKM, and LTP.
[2] Compute refers to the processing power and resources required to train, deploy, and run AI models
[3] For illustrative purposes only
[4] For illustrative purposes only
[5] Markets and Markets. Data as of 2023, projected through 2030.
[6] Grayscale Investments as of August 8, 2024. Represents “Universe” of AI-related crypto assets based on Grayscale Research Methodology.
[7] 45 subnets as of August 14, 2024 (source)